[2025 -08- 05]
As industries across Malaysia and beyond intensify efforts toward smart manufacturing, 2025 is shaping up to be a breakthrough year for industrial automation. Fueled by government policies, technological innovation, and a growing need for operational resilience, manufacturers are embracing advanced solutions to stay competitive. At PilotWorks-IAS, we empower this transformation with cutting-edge automation services designed to meet the evolving needs of our clients.
Here are the top 10 automation trends redefining the future of manufacturing in 2025 backed by expert insights and data.

Image used under license from iStock.
1. AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance, driven by AI and machine learning, is minimizing unplanned downtimes and extending equipment life. In 2025, it has become a must-have strategy for manufacturers striving for operational efficiency and cost control.
By analyzing real-time sensor data and historical machine logs, AI algorithms can predict component failures before they happen, allowing teams to schedule timely interventions and avoid expensive stoppages. This technology is especially impactful in high-value sectors like automotive, semiconductors, and precision manufacturing [3].
As reported by The Star, Malaysia’s federal government is fueling this transformation by allocating RM50 million toward AI-related education in Budget 2025, a strategic move that strengthens local capability for implementing intelligent industrial systems [2]. This aligns with national initiatives like Industry4WRD, which promotes AI-enabled automation as a core productivity driver [1].
Custom visual used under license.
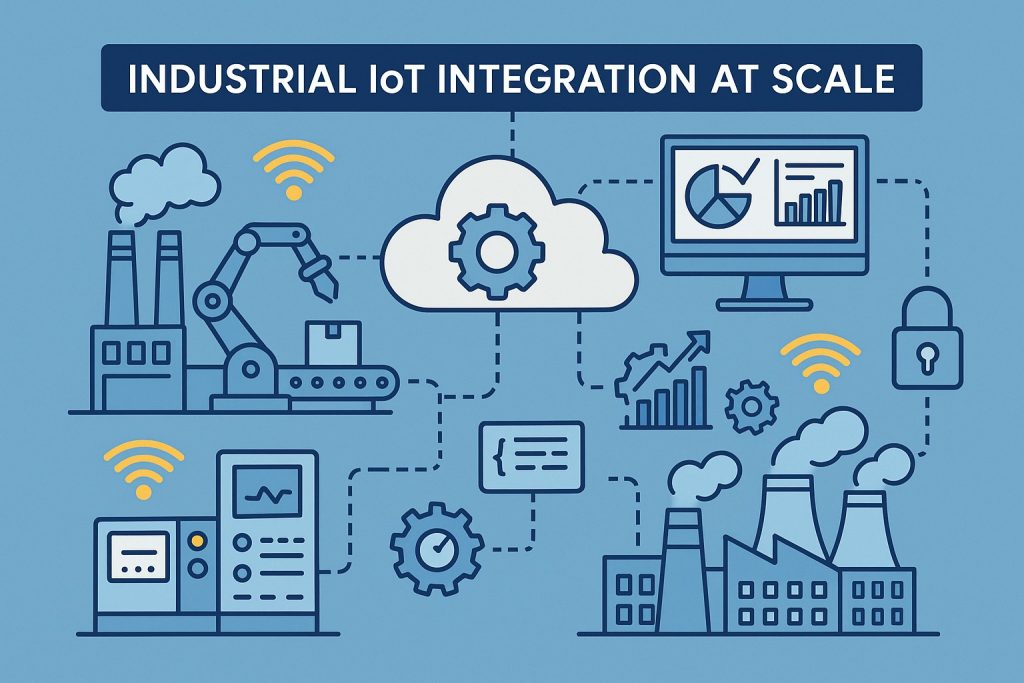
2. Industrial IoT (IIoT) Integration at Scale
Industrial IoT (IIoT) is rapidly reshaping Malaysia’s manufacturing sector by connecting machines, sensors, and systems into unified data ecosystems. In 2025, manufacturers are moving beyond pilot projects toward full-scale IIoT integration, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and smarter decision-making.
The Ministry of International Trade and Industry’s Industry4WRD policy supports this push toward widespread IIoT adoption across Malaysia [1]. It promotes the deployment of smart sensors and connected systems to improve process visibility, output quality, and automation-readiness. This aligns with Malaysia’s target of building 3,000 smart factories and boosting productivity by 30% per worker by 2025 [1].
IIoT implementation has been particularly transformative for SMEs, where cost-effective sensors and cloud platforms help level the playing field. Many companies are now engaging with automation solution providers to deploy plug-and-play IIoT modules with minimal disruption [3].

Source: Laws of Malaysia – Attorney General’s Chambers (AGC)
3. Cybersecurity for Industrial Control Systems
As industrial automation expands, so does the attack surface. In 2025, cybersecurity is no longer optional, it’s a core requirement for protecting industrial control systems (ICS), programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and factory networks from increasingly sophisticated threats.
The Cyber Security Act 2024 (Act 854) establishes new regulatory frameworks to enhance critical infrastructure protection, including in sectors like manufacturing, energy, and logistics [4]. This legislation introduces clearer responsibilities for OT cybersecurity and incident response, signaling the government’s growing emphasis on digital safety.
Cyberattacks targeting industrial systems, such as ransomware, data manipulation, or remote sabotage, can halt production, compromise safety, and lead to major financial losses. Malaysian factories, particularly those integrating IIoT and remote access, are now adopting network segmentation, encryption protocols, and continuous monitoring tools to stay secure [3].

Image used for illustrative purposes only. Licensed via iStock.
4. 5G and Edge Computing in Smart Factories
To keep up with real-time industrial demands, manufacturers are now integrating 5G and edge computing, creating faster, more responsive smart factories in Malaysia and globally. These technologies reduce latency, improve data handling at the machine level, and enable time-sensitive applications like robotics, vision inspection, and remote maintenance.
As announced in early 2024, MCMC and MIDA have partnered to accelerate industrial 5G adoption, focusing on high-impact sectors like manufacturing and logistics [5]. This initiative includes testbeds and advisory support for companies to integrate private 5G networks and edge nodes.
By processing data closer to the source, edge computing minimizes reliance on centralized cloud servers. This allows systems like AGVs (automated guided vehicles) and real-time quality control tools to respond instantly, even in environments with limited connectivity.
Infographic created for illustrative purposes.
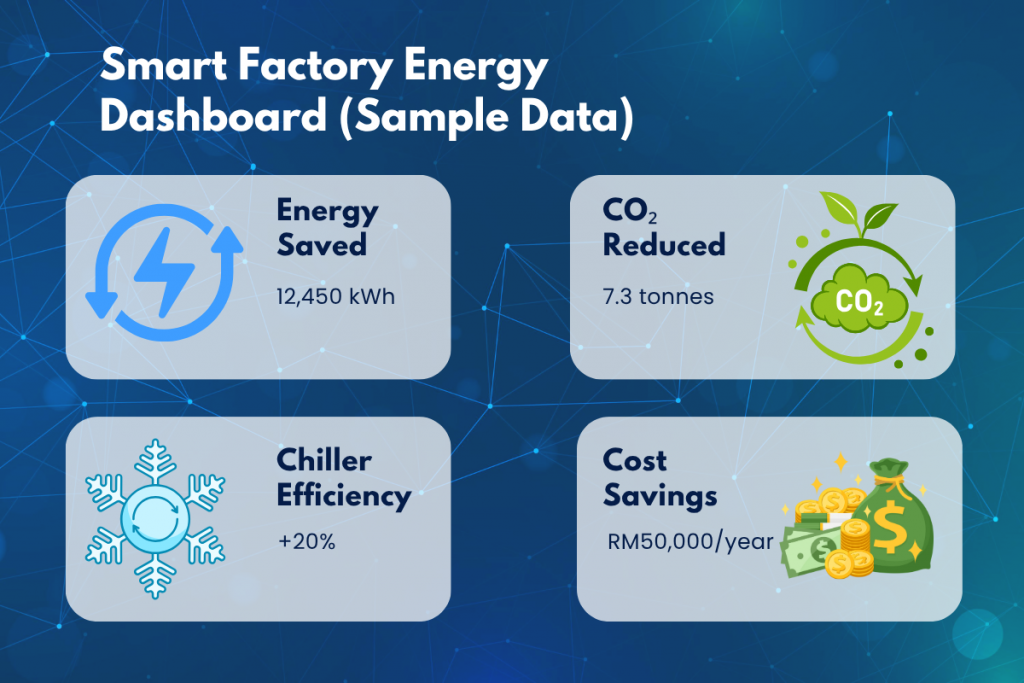
5. Energy-Efficient Automation
As energy costs rise and sustainability targets tighten, energy-efficient automation is taking center stage in 2025. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting smart sensors, variable speed drives (VSDs), and AI-driven energy optimization tools to reduce electricity consumption without compromising output.
Malaysia’s SAVE 4.0 program, led by the Sustainable Energy Development Authority (SEDA), reflects the government’s broader push toward energy-conscious industrial practices. While originally focused on chillers and building systems, its principles are now inspiring broader energy efficiency standards in manufacturing [6].
Modern automation solutions including real-time power monitoring and energy-aware control algorithms are helping industries track usage, detect inefficiencies, and dynamically adjust operations. This shift not only reduces environmental impact but also improves long-term profitability and ESG compliance.
6. Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology is revolutionizing industrial automation by creating real-time virtual models of physical assets, systems, or entire facilities. These digital replicas enable better monitoring, simulation, and optimization improving performance, predicting failures, and supporting remote diagnostics.
In Malaysia, Schneider Electric and Air Selangor launched the country’s first digital twin for water treatment, marking a major milestone in national adoption [7]. The initiative demonstrates how local industries are leveraging this technology to enhance operational intelligence and resource efficiency.
Digital twins are particularly valuable for high-stakes environments such as manufacturing plants, where predictive modeling can reduce downtime and improve safety. As data integration and cloud platforms advance, digital twin deployments are expected to expand rapidly in 2025.
7. Collaborative Robots (Cobots) on the Rise
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are transforming production lines by working safely alongside human operators. In contrast to traditional robots, cobots are designed for flexibility, adaptability, and ease of deployment making them ideal for small-batch, mixed-model, and labor-intensive tasks.
According to the Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA), cobots are pivotal in Malaysia’s strategy to modernize SMEs and boost automation adoption across key manufacturing sectors [8]. Their user-friendly interfaces and minimal safety barriers help companies automate without major structural changes.
In 2025, cobots are being deployed in electronics assembly, automotive inspection, and even packaging tasks offering precision, consistency, and improved ergonomics. PilotWorks is among the automation solution providers promoting safe human-machine collaboration through cobot integration.
8. Hyperautomation & Low-Code Platforms
In 2025, manufacturers are embracing hyperautomation a strategy that combines robotic process automation (RPA), AI, and low-code tools to automate virtually every process possible. It goes beyond factory machinery, extending into supply chains, reporting, and administrative workflows.
According to Business Today, hyperautomation is gaining traction in Malaysia’s digital transformation plans, especially within large-scale manufacturing where data integration and speed are critical [9]. By using low-code platforms, companies can now build automation workflows faster and at lower cost even without deep coding expertise.
Hyperautomation helps unify fragmented systems, reduce human error, and scale automation across departments. For SMEs, this approach offers a bridge between manual operations and intelligent automation, improving agility and efficiency.
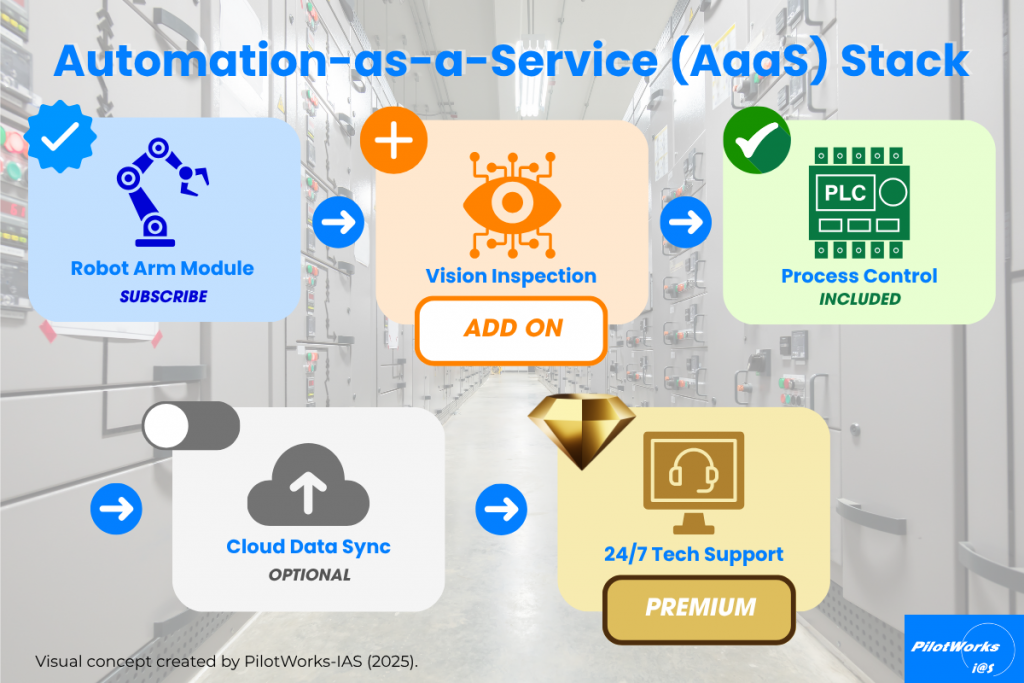
9. Automation-as-a-Service (AaaS)
Automation is evolving from capital-heavy infrastructure into a service-based model, where manufacturers can subscribe to automation technologies instead of purchasing them outright. This shift known as Automation-as-a-Service (AaaS) lowers entry barriers for SMEs and enables faster scalability.
In Malaysia, the MIDF Smart Automation Grant introduced by MIDA supports this transition by offering co-funding for automation systems that improve productivity and reduce reliance on manual labor [10]. AaaS models are particularly attractive for smaller manufacturers that need agility and cost flexibility.
With AaaS, companies can access modular automation tools from cloud-based robotics to remote monitoring systems and scale them up or down as needed. This “plug-and-play” approach allows firms to pay only for what they use, turning automation into an operating expense rather than a long-term investment.

Source: The Borneo Post (2024)
10. Workforce Upskilling & Human-Automation Synergy
Malaysia’s industrial transformation relies not only on technology, but on people. As automation adoption accelerates, the need for a digitally fluent workforce becomes urgent. Ongoing investments in TVET and STEM education aim to equip Malaysians with practical skills and advanced knowledge for future-ready jobs [1][2].
Key government initiatives such as the Industry4WRD Readiness Assessment, Digital Economy Blueprint, and TVET enhancement programmes reflect a strong push to cultivate a high-skilled workforce [1]. Simultaneously, RM50 million has been allocated in Budget 2025 to enhance AI education through Malaysia’s research universities [2].
At a recent event in Sabah, education leaders emphasized improving synergy between TVET and STEM pathways to better align with automation industry demands, particularly through enhanced collaboration between public and private sectors [11]. This reflects a broader national goal: preparing 3,000 smart factories and a digitally skilled manufacturing workforce by 2025 [1].
Government Framework & Support for 2025
Malaysia’s government is actively shaping the industrial automation landscape through strategic frameworks, funding programs, and national talent development efforts. These initiatives directly support the Top 10 trends highlighted in this article:
🔹 Industry4WRD Policy
MITI’s national framework for Industry 4.0 provides structured guidance on automation, digitalisation, and productivity enhancement.
📌 Targets: 3,000 smart factories, 30% productivity boost per worker by 2025
[1]
🔹 Budget 2025 Commitments
• RM10 million allocated to the National AI Office
• RM50 million set aside for AI education at research universities
[2]
🔹 MIDF Smart Automation Grant
A government co-funding initiative to accelerate automation adoption, especially among SMEs.
[10]
🔹 TVET and STEM Investment
The government continues investing in technical and vocational education, with renewed focus on AI-readiness and industrial workforce upskilling.
[11]
Conclusion
Industrial automation in 2025 is being driven by powerful technologies and strong national support. With trends like AI, IIoT, and cobots gaining traction and frameworks like Industry4WRD and Budget 2025 fueling progress Malaysia is well positioned to lead in smart manufacturing.
At PilotWorks-IAS, we’re committed to helping industries embrace this future with practical, scalable automation solutions. Whether you’re starting small or scaling up, we’re here to support your digital transformation.
Contact us to explore how we can automate your operations.
📧 Email: sales@my-ias.com
📞 Phone: +60 7-562 1221
💬 WhatsApp: +60 16-728 9469
📍 47, Jalan Flora 1/9, Taman Pulai Flora, 81300 Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
🌐 Website:https://my-ias.com
References
- Ministry of International Trade and Industry. (2023). Industry4WRD: National policy on Industry 4.0. https://www.miti.gov.my/industry4wrd
- The Star. (2024, October 18). AI-related education to be expanded with RM50mil allocation. https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2024/10/18/ai-related-education-to-be-expanded-in-all-research-universities-with-rm50mil-allocation-says-pm
- Malaysian Investment Development Authority. (2025). Automation key enabler in digitalisation of manufacturing. https://www.mida.gov.my/mida-news/automation-key-enabler-in-digitalisation-of-manufacturing/
- Laws of Malaysia. (2024). Cyber Security Act 2024 (Act 854). Attorney General’s Chambers. https://lom.agc.gov.my/ilims/upload/portal/akta/outputaktap/2177706_BI/Act%20854.pdf
- Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission. (2024, March 18). MCMC and MIDA forge strategic partnership on 5G for industry. https://www.mida.gov.my/events/mcmc-and-mida-forge-strategic-partnership-to-propel-5g-adoption-in-malaysia/
- Sustainable Energy Development Authority. (2025). SAVE rebate program (chiller) guidelines [Unpublished internal document].
- Schneider Electric. (2025, March 12). Malaysia launches first digital twin for water treatment. https://www.se.com/my/en/about-us/newsroom/news/press-releases/air-selangor-and-schneider-electric-reinforce-water-security-with-malaysia’s-first-digital-twin-water-treatment-plant-wtp-67c94f49ebfa6a5dd90975c3
- Malaysian Investment Development Authority. (2023). Collaborative robotics and advanced automation for SMEs. https://www.mida.gov.my/mida-news/robotics-and-advanced-automation-pivotal-in-new-industrial-master-plan-transformation/
- Business Today. (2024, April 15). Hyperautomation trend in Malaysia manufacturing. https://businessnews.com.my/2024/04/15/hyperautomation-malaysian-digital/
- Malaysian Investment Development Authority. (2024). MIDF Smart Automation Grant empowers SMEs. https://www.mida.gov.my/mida-news/budget-2025-to-accelerate-malaysias-digitalisation-ai-adoption/
- The Borneo Post. (2024, June 21). STEM, TVET can still be improved in Sabah: Prof. https://www.theborneopost.com/2024/06/21/stem-tvet-can-still-be-improved-in-sabah-prof/
